The term “traumatic brain injury” is a broad umbrella encompassing a wide range of injuries to the brain. These injuries can be mild with little impairment or long-term effect, or they can severe, even leading to coma or death.
These types of injuries come in two forms:
- Closed brain injury. This type of brain injury does not cause the skull to be broken into. The brain is damaged by severe movement that causes the brain to shake or move back and forth within the skull. That in turn leads to the brain’s tissues and blood vessels becoming bruised or torn.
- Penetrating brain injury. In this type of brain injury, also known as an open-head injury, the skull is broken and the brain damaged from an external source.
What Causes a Traumatic Brain Injury?
Anything that causes the brain to be vigorously moved within the skull or causes the skull to break can cause a traumatic brain injury.
Some common events that cause these injuries include:
- Falling or tripping
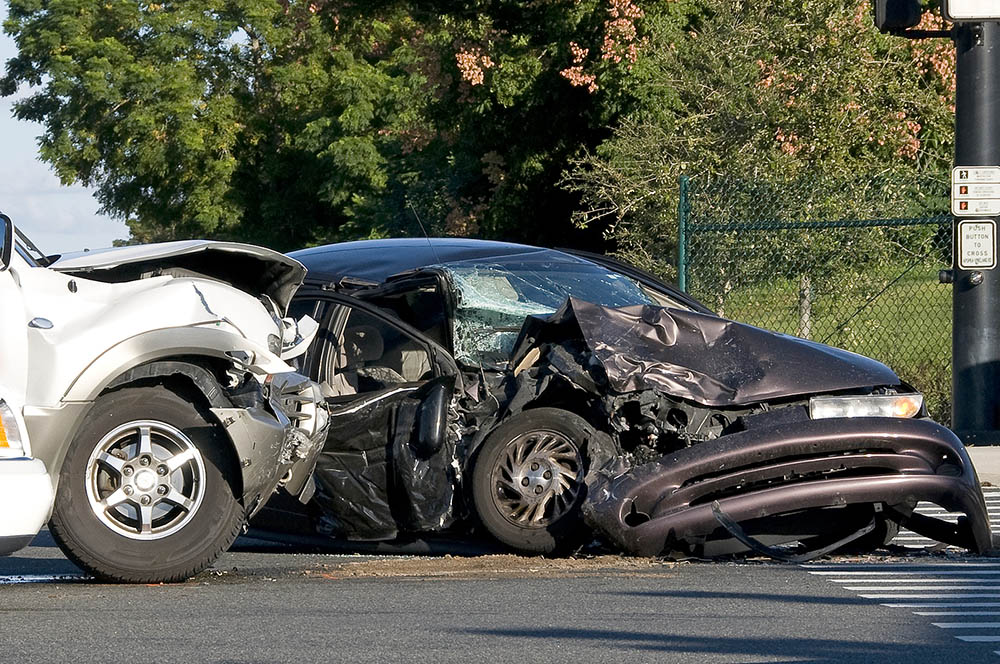
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Assault
- Gunshots
- Shaken baby syndrome
- Sports
- Being struck by an object
- Explosions
When Do Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injury Appear?
Traumatic brain injuries are complex and varied. In some cases, there are mild symptoms that eventually dissipate. In other cases, there are long-term or even permanent results. Some symptoms appear immediately, while others may not manifest for days or weeks.
Injuries that cause symptoms right away are called primary brain injuries. For example, if someone is in a car accident that causes a concussion, that manifests immediately. There are also injuries called secondary brain injuries, which happen after the event and involve slower changes of the blood vessels, tissues, cells, or chemicals in the brain. These kinds of injuries may not show symptoms right away.
Are Traumatic Brain Injuries and Concussions the Same Thing?
Traumatic brain injury is a large category of brain injuries with different levels of severity and signs or symptoms. A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury. Many medical professionals refer to concussion as a mild traumatic brain injury, although concussions can be severe.
What Kinds of Symptoms Are Caused by Traumatic Brain Injury?
There is a wide range of symptoms that can accompany a traumatic brain injury, showing up either immediately or within hours or days.
The symptoms are sorted by the medical community into mild or moderate to severe. These are the common symptoms in both categories.
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
- Headache
- Nausea
- Dizziness or lack of balance
- Difficulty speaking
- Fatigue
- Loss of consciousness for up to a few minutes, or being in a state of confusion or feeling dazed
- Either difficulty sleeping or sleeping more than usual
- Elevated moodiness
- Trouble remembering or concentrating on things
- Light or sound sensitivity
- Blurred vision or ringing in the ears
Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
Moderate to severe traumatic brain injury can have any of the symptoms listed under mild injury, but they can be joined by the following:
- Loss of consciousness for several minutes up to hours
- Seizures
- Inability to stay awake
- Headache that lasts or worsens
- Repeated vomiting or severe nausea
- Extreme confusion or agitation
- Slurred speech
- Dilation of one or both pupils in the eyes
- Clear fluids coming from the nose or ears
- Weak or numb fingers and toes
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injury in Young Children
If a child is too young to be able to tell you they have any of the above symptoms, watch for the following:
- Persistent crying
- Seizures
- Noticeable changes in sleeping habits
- Drowsiness
- Seeming unusually sad or irritable
- Change in eating habits
- Reduced interest in toys and activities
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Traumatic Brain Injury?
While many people find the symptoms they suffered at the time of the traumatic brain injury reduce and disappear with time and treatment, there are also many people who have long-term or permanent damage. These changes can be both physical and psychological.
- Motion sickness
- Anxiety or feeling overwhelmed
- Difficulty concentrating, easily distracted
- Depressing
- Low energy
- Memory loss
- Heightened irritability
- Light or sound sensitivity
- Easily fatigued or cannot sleep properly
- Mood and personality changes
- Difficulty controlling impulses or with executive function
Can a Traumatic Brain Injury Cause Me to Be Disabled?
Yes. More severe traumatic brain injuries can have long-term or permanent repercussions that can disrupt your day-to-day and work lives, possibly to the extent that you can no longer work or can work fewer hours or at a different, less-lucrative job.
The types of symptoms that can cause disability include impaired memory (either short- or long-term), trouble with focus or thinking, personality changes (especially involving increased irrational anger or aggression) or mood swings, difficulty with impulse control or making decisions, anxiety or depression, or post-traumatic stress.
If your ability to earn a living has been affected by a traumatic brain injury, and that injury was caused by another person or entity, seeking legal redress is recommended.
What Should I Do if I or a Loved One Suffered a Traumatic Brain Injury?
Call me as soon as possible at 303-500-1376 to request a free case evaluation. Don’t talk to the other party’s lawyer or insurance company. Their lawyer and insurance representative are looking out for their best interests, not yours. They’re also going to try and defer the blame, possibly back onto you. They will try to get you to inadvertently admit the fault was yours, not theirs.
Traumatic brain injury can have many causes and outcomes, some of which can be catastrophic. If someone or something else is at fault for your injury, they may be liable, which could lead to you receiving a financial settlement that could be needed for ongoing medical and psychological treatment.